How the Pogo Pin Works
First, the pogo pins were never designed to have high-speed data transfer. Let's take a look at how a pogo pin works, the mating end of the contract is usually gold plated and is usually a pointed point. The connection is made when this sharp point is pressed against the usually softer "mating contact". With no wiping action, as with standard pin and socket contacts, this design is more susceptible to contamination and corrosion, increasing the contact resistance across the connection, which makes low-voltage, high-speed signals more difficult to transmit.
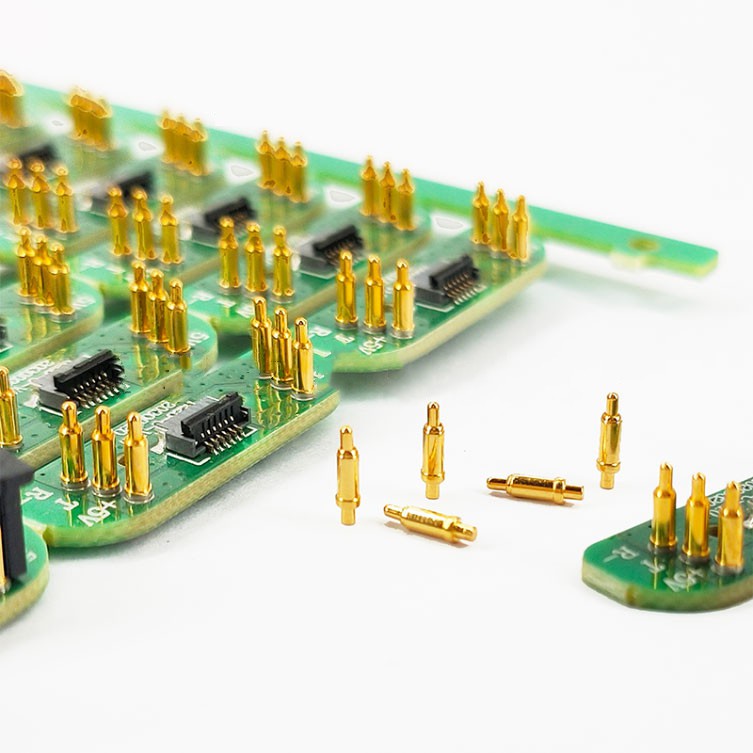
The second design issue is the internal spring. The spring must make good contact with the plunger and base of the pogo pin, which can be problematic. Due to its helical design, the spring also introduces inductance into the contacts. Finally, to overcome the problems of using these contacts in a matched impedance system, each signal circuit must be surrounded by several ground circuits to isolate the contact's signal path from surrounding signal paths.
