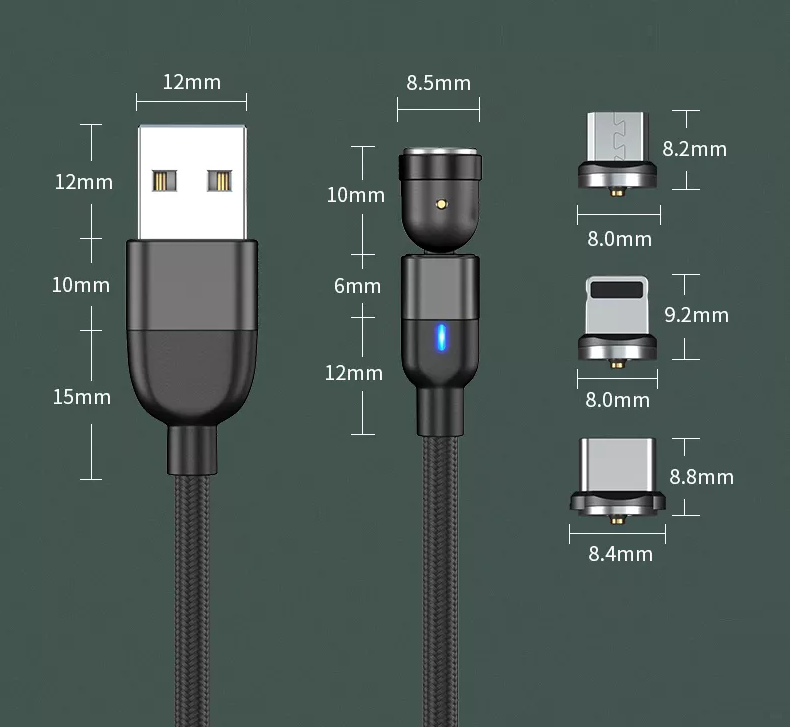
Type-C Pogo Pin Connector
The type-C connector is a single connector solution for data, power, and A/V applications, its slim profile is suitable for mobile devices, and it is durable enough for industrial applications. -C interface, because of the increasing application scenarios of Type-C connectors, performance requirements will be imposed on factors such as high-frequency signals, mechanical characteristics, electrical performance, and environmental changes. Therefore, manufacturers need a complete set of tests when producing related products. The certification plan and the assistance and consultation of professional laboratories (industry information丨GRL expands the Dongguan laboratory and adds new testing capabilities) can ensure that the products meet the quality conditions and perfectly display the functional requirements; professional laboratories and certification bodies will also Test (Electrical Test), Mechanical Test (Mechanical Test), and Environmental Test (Environmental Test) required test content to do the relevant test verification to ensure that the manufacturer's products can meet the standards of the association, the manufacturer in the associated certification and testing center verified In the process, the production parameters will also be harvested to facilitate subsequent production; to ensure the reliability and continuity of the product, today we will briefly understand the production process of this interface

A brief description of the manufacturing process of Type-C connectors, the process can be divided into four main manufacturing steps: stamping, electroplating (PlaTIng), injection molding (Molding), and assembly (Assembly).
Stamping
The manufacturing process for Type-C connectors usually starts with a stamped plug. Stamping is based on large and medium-sized high-speed stamping machines, and Type-C connectors (plugs) are stamped from thin metal strips. One end of the large coil of metal strip is sent to the front end of the punching machine, and the other end is wrapped around the eccentric wheel across the hydraulic press operating table of the punching machine.

Electroplating process (PlaTIng)
After the connector pin stamping is completed, the next process is the electroplating process (PlaTIng); at this stage, the electronic contact surface of the connector will be coated with various metal material coatings, nickel electroplating, tin electroplating, and semi-gold plating, Avoid air oxidation and improve conductivity. A problem similar to the stamping stage, such as pin twisting, breaking, or deformation, also occurs when stamped pins are fed into electroplating equipment. The pins will also be distorted, cracked, or deformed during the whole process of feeding the stamped pins into the electroplating equipment. And the shortcomings of this quality are very easy to detect based on the above technology. However, for most machine vision system suppliers, many quality defects in the electroplating process remain a "no-go zone" for inspection systems. Type-C connector manufacturers want inspection systems that can detect a variety of inconsistent defects, such as small scratches and pinholes, on the plated surfaces of connector pins. While these defects are easily identified on other products (such as aluminum can bottoms or other relatively flat surfaces); due to the irregular and angled surface design of most Type-C connectors, it is difficult for visual inspection systems to identify these subtle defects required Image.

Injection molding (Molding)
Injection molding (Molding) refers to the plastic box seat of the electronic USB connector formed by introducing molten plastic into the metal material tire film, and then rapidly refrigerating and forming. When molten plastic fails to fill the membrane, so-called "leakage" occurs; this is a typical defect that needs to be detected at the injection molding stage. Other defects include filling or partially plugging the sockets (these must be kept clean and smooth for proper connection to the pins after assembly). Machine vision systems for post-injection quality inspection are relatively simple to implement, as leaks in cartridge holders and plugged jacks can be easily identified using a backlight. It is a typical defect that must be checked in the injection molding process. Other disadvantages include full or partial blockage of the sockets (which must be kept clean and unobstructed for proper mating with the pins in final assembly).

Assembly
The final process of Type-C connector manufacturing is the finished product assembly (Assembly). There are two ways to connect and assemble the pins with the electroplating process and the injection-molded box seat: individual plugs or combined plugs. One pin is connected at a time; the combination plug is formed into a pair of plugs to form a pair of plugs, which means that several pins are connected to the box socket at a time. No matter which connection method is used to assemble, the manufacturer needs to detect whether all the plugs have leakage and correct positioning during the assembly stage, to ensure that all pins cannot have all errors and leaks and the precise positioning must be appropriate.

Type-C connector test verification process
Insertion force
The connector insertion force test refers to the force required to insert and pull out the electronic connectors at both ends of the mating male and female ends. The following tests apply to the insertion force, extraction force, plastic retention force, and use The plug-in force is an important mechanical property and parameter of the connector, and its size affects the feel of the connector and its internal design structure. At present, the plug-in force of the board-to-board connector, which is the most widely used mobile phone, The shrapnel microneedle module that can transmit current and conduction signal can be used in the test, which is beneficial to the stability of the test. It can transmit a large current in the range of 1-50A, the overcurrent is stable and smooth, and it has a good connection function. Now we want to For the insertion force test, we first test the durability 10,000 times, and the conditions are 200 times for one hour and fifty hours.
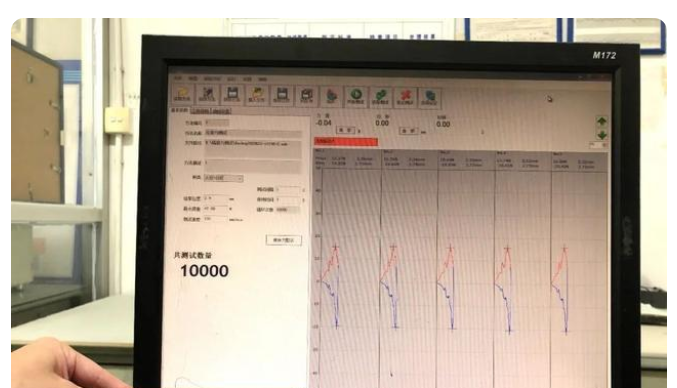
The test time is 50 hours, with an average of 200 times an hour
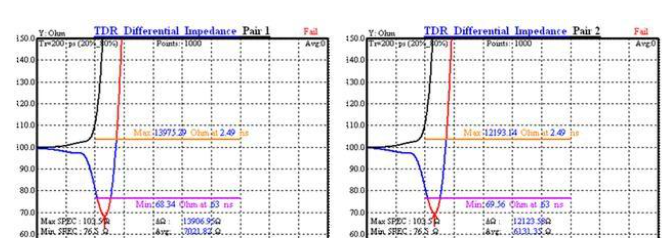
high-frequency test
In terms of function, the USB used to be just a cable, but with the intervention of the Emark chip of USB3.1, the cable today should be said to be a link device, so the complexity is completely different. The functions on the chip must be more powerful (encoding, compression, etc.), but in fact, most of the current USB cables are always online, and the function is to transmit data (the actual high-frequency requirements of the plug have little impact on the transmission of data. Therefore, except for the part sent to the association for testing, the normal mass-produced connectors do not test the high-frequency impedance performance), charging the device (currently the biggest function of our application is to charge the device, although there is a data function, the actual application scenario is very If you want to protect these functions, you need to start from the design and production application of the connector, so there are many design applications in the connector. Materials, insulation, prevention of short circuits between terminals and shells, and some low-cost connectors are likely to be omitted directly. They are called combat version connectors. Manufacturers with quality requirements are not recommended to use them, and there will be endless troubles.